| Embryology: Stage III | |
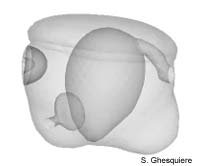 Embryo in Stage 3. |
|
Interactive 3D-models (Java): |
The embryo has grown to about 190µm in Marisa cornuarietis, while
the Pila globosa embryo hasn't notably increased in length. The embryos
of both species are now more elongated than in the previous stage.
Externally, the embryo is still bilateraly symmetrical, but internally the arangement
of organs and structures have become assymetrical.
At the front side of the embryo, the foot has become more prominent, jus like
the visceral sac at the posterior side. The shell gland and plate, also defined
as the rudimental shell has increased in size and forms a cup-shaped invagination
on the posterior side, below the border of the velum.
In stahe II, the stomodaeum at the anterior (front) side of the embryo already
started to become conspicuous as a invagination. This invagination progresses
in this stage (III) and ultimately makes contact with the archenteron or primitive
stomach. With this event, the intestinal system opens at the front side of th
embryo, thus enabling it to take up yolk from the egg through the intestines.
Also at the front side of the embryo, the head plates become differentiate further,
making the better visible than in the previous stage.
Back to the posterior side of the embryo, the development of the excretion system
becomes visible as the rudimental ureter and renal vestibule invaginate. In
stage II these organs were only a small, hard to spot, cell plate.
Internally the mesoderm plate differntiates to form the pericard (heart-sac)
and the kindey. The latter will make contact with the rudimental ureter in a
later stage. The left aggregate of mesoderm cells, developed in stage II, disappear
during this stage.
The primitive stomach, now communicating with the stomodaeum develops cilated
cells a the surface of the roof.
As mention before the embryo has become internally asymetric during this stage,
due to the diminishing of the left mesoderm plate, while the right one developed
into thje pericard and kidney.
|
Except where otherwise noted, this page is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 2.5 License . http://www.applesnail.net |
|